Research
| Line 207: | Line 207: | ||
<span class="plainlinks"> | <span class="plainlinks"> | ||
| − | [[File:PPT.jpg|60px|link=]] | + | [[File:PPT.jpg|60px|link=http://www.ecc.itu.edu.tr/images/e/eb/Comert_Yadavari_Altun_Erturk_Reliability_Prediction_of_Electronic_Boards_by_Analyzing_Field_Return_Data.pptx]] |
</span> | </span> | ||
| − | <br> Slides | + | <br> [http://www.ecc.itu.edu.tr/images/e/eb/Comert_Yadavari_Altun_Erturk_Reliability_Prediction_of_Electronic_Boards_by_Analyzing_Field_Return_Data.pptx Slides] |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 10:50, 25 September 2014
Our research aims to develop novel ways of computing, circuit design, and reliability for electronic circuits and systems. Our research mainly targets future and emerging technologies.
Contents |
Computing with Switching Nano Arrays | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
As current CMOS-based technology is approaching its anticipated limits, research is shifting to novel forms of nanoscale technologies including molecular-scale self-assembled systems. Unlike conventional CMOS that can be patterned in complex ways with lithography, self-assembled nanoscale systems generally consist of regular structures. Logical functions are achieved with crossbar-type switches. Our model, a network of four- terminal switches, corresponds to this type of switch in a variety of emerging technologies, including nanowire crossbar arrays and magnetic switch-based structures. SynthesisIn his seminal Master's Thesis, Claude Shannon made the connection between Boolean algebra and switching circuits. He considered two-terminal switching networks to implement any Boolean function that is the foundation of CMOS circuit design techniques. In this work, we have considered four-terminal switching networks to implement any Boolean function that aims to be a foundation of nano array based circuit design techniques. 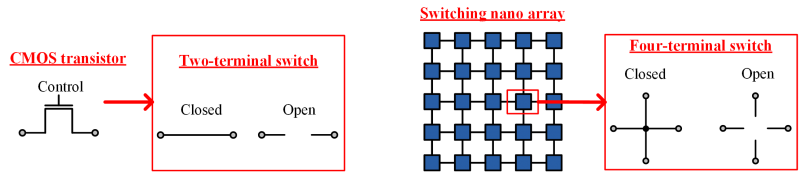 ReliabilityWe have devised a novel framework for digital computation with networks of nanoscale switches with high defect rates, based on the mathematical phenomenon of percolation. With random connectivity, percolation gives rise to a sharp non-linearity in the probability of global connectivity as a function of the probability of local connectivity. This phenomenon is exploited to compute Boolean functions robustly, in the presence of random defects.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reliability of Electronic Boards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The rapid developments in electronics, especially in the last decade, have initiated the inception of electronics reliability . Conventionally used accelerated reliability tests have lost their significance; time consuming and expensive feature of these tests is against the demands of today's very rapid electronic product cycles. In this study, we propose less costly, yet accurate, reliability prediction techniques using field return data, new accelerated test methodologies, and physics of failure based simulations. We cooperate with one of the Europe’s largest household appliances companies Arçelik A.Ş.. 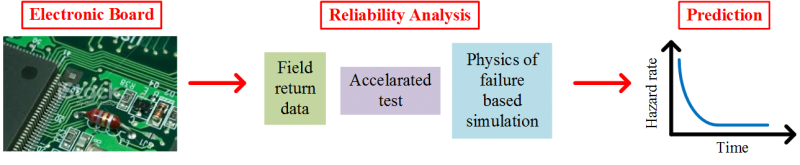 Field Data Analysis and PredictionWe perform field return data analysis of electronic boards having two steps filtering and modeling. In the first step of filtering we eliminate improper data, consisting of obvious and hidden errors, from the whole field return data. In the second step of modeling, we use the filtered data to develop our piecewise reliability model. Our reliability analysis is based on a new technique that deals with forward and backward time analysis of the data. We precisely predict the reliability performance of electronic boards throughout the warranty period by using very short-term field return data. For electronic boards targeted in this study, warranty period is 3 years, and we use field data of 3 months.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantum Circuit Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Synthesis and OptimizationWe propose a fast synthesis algorithm that implements any given reversible Boolean function with quantum gates. Instead of an exhaustive search on every given function, our algorithm creates a library of essential functions and performs sorting. As an example, to implement 4 bit circuits we only use 120 essential functions out of all 20922789888000 functions. By considering the physical structure of quantum gates, we show that optimum area solutions proposed in the literature are not actually optimum; they can be improved.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Analog Circuit Design | |||||||||||||||
Positive FeedbackThe conventional wisdom is that analog circuits should not include positive feedback loops. As controversial as it seems, we have successfully used positive feedback for impedance improvement in a current amplifier. With adding few transistors we have achieved very low input resistance values. Additionally, we have proposed a new fully-differential current amplifier and tested it in a filter application.
| |||||||||||||||
Discrete Mathematics | |||||||||||||
Self Duality ProblemThe problem of testing whether a monotone Boolean function in irredundant disjuntive normal form (IDNF) is self-dual is one of few problems in circuit/time complexity whose precise tractability status is unknown. We have focused on this famous problem. We have shown that monotone self-dual Boolean functions in IDNF do not have more variables than disjuncts. We have proposed an algorithm to test whether a monotone Boolean function in IDNF with n variables and n disjuncts is self-dual. The algorithm runs in O(n^3) time.
| |||||||||||||

